DRAFT CPSC Bicycle Helmet Standard
as of December, 1997
This is history! See below.
Summary: The final draft of the Consumer Product Safety Commission's bicycle helmet standard for approval by the Commissioners. This was not an official copy, but our carefully-proofed scan of material from the CPSC Commission briefing packet. This is for historic interest, since you can now access the final standard.
Part 1203 - SAFETY STANDARD FOR BICYCLE HELMETS
Subpart A - - The Standard
1203.1 Scope, general requirements, and effective date.
1203.2 Purpose.
1203.3 Referenced documents.
1203.4 Definitions.
1203.5 Construction requirements - projections.
1203.6 Labeling and instructions.
1203.7 Samples for testing.
1203.8 Conditioning environments.
1203.9 Test headforms.
1203.10 Selecting the test headform.
1203.11 Marking the impact test line.
1203.12 Test requirements.
1203.13 Test schedule.
1203.14 Peripheral vision test.
1203.15 Positional stability test (roll-off resistance).
1203.16 Dynamic strength of retention system test.
1203.17 Impact attenuation test.
1203.2 Purpose.
1203.3 Referenced documents.
1203.4 Definitions.
1203.5 Construction requirements - projections.
1203.6 Labeling and instructions.
1203.7 Samples for testing.
1203.8 Conditioning environments.
1203.9 Test headforms.
1203.10 Selecting the test headform.
1203.11 Marking the impact test line.
1203.12 Test requirements.
1203.13 Test schedule.
1203.14 Peripheral vision test.
1203.15 Positional stability test (roll-off resistance).
1203.16 Dynamic strength of retention system test.
1203.17 Impact attenuation test.
Subpart B - - Certification
1203.30 Purpose and scope.
1203.31 Effective date.
1203.32 Definitions.
1203.33 Certification testing.
1203.34 Product certification and labeling by manufacturers (including importers).
1203.31 Effective date.
1203.32 Definitions.
1203.33 Certification testing.
1203.34 Product certification and labeling by manufacturers (including importers).
Subpart C - - Recordkeeping
1203.40 Effective date.
1203.41 Recordkeeping requirements.
1203.41 Recordkeeping requirements.
Subpart D -Bicycle Helmets Manufactured From March 16, 1995, Through [insert date that is 1 Year after
publication].
1203.5,1 Purpose.
1203.52 Scope and effective date.
1203.53 Interim safety standards.
1203.52 Scope and effective date.
1203.53 Interim safety standards.
Figures for Part 1203
AUTHORITY: 15 U.S.C. 2056, 2058, and 6001-6006.
Subpart B is also issued under 15 U.S.C. 2063.
Subpart C is also issued under 15 U.S.C. 2065.
Subpart A-The Standard
§1203.1 Scope, general requirements, and effective date.
(a) Scope. This standard describes test methods and defines minimum performance criteria for all bicycle
helmets, as defined in §1203.4(b).
(b) General requirements.
(c)Effective date. The standard shall become effective [insert date that is 1 year after publication] and shall apply to all bicycle helmets manufactured after that date. Bicycle helmets manufactured between March 16, l995, and [insert date that is 1 year after publication], inclusive, are subject to the requirements of Subpart D, rather than this Subpart A.
(b) General requirements.
(i) Projections. All projections on bicycle helmets must meet the construction requirements of §
1203.5
(ii) Labeling and instructions. All bicycle helmets must have the labeling and instructions required by § 1203.6.
(iii) Performance tests. All bicycle helmets must be capable of meeting the peripheral vision, positional stability, dynamic strength of retention system, and impact attenuation tests described in § 1203.7-1203.17.
(iv) Units. The values stated in International System of Units ("SI") measurements are the standard. The inch-pound values stated in parentheses are for information only.
(ii) Labeling and instructions. All bicycle helmets must have the labeling and instructions required by § 1203.6.
(iii) Performance tests. All bicycle helmets must be capable of meeting the peripheral vision, positional stability, dynamic strength of retention system, and impact attenuation tests described in § 1203.7-1203.17.
(iv) Units. The values stated in International System of Units ("SI") measurements are the standard. The inch-pound values stated in parentheses are for information only.
(c)Effective date. The standard shall become effective [insert date that is 1 year after publication] and shall apply to all bicycle helmets manufactured after that date. Bicycle helmets manufactured between March 16, l995, and [insert date that is 1 year after publication], inclusive, are subject to the requirements of Subpart D, rather than this Subpart A.
§ 1203.2 Purpose and basis.
The purpose and basis of this standard is to reduce the likelihood of serious injury and death to bicyclists
resulting from impacts to the head, pursuant to 15 U.S.C. 6001-6006.
§ 1203.3 Referenced documents.
(a) The following documents are incorporated by reference in this standard.
(b) This incorporation by reference was approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51. Copies of the standards may be obtained as follows. Copies of the draft ISO/DIS Standard 6220-1983 are available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036. Copies of the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 218, Motorcycle Helmets, are available from the Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Office of Vehicle Safety Standards, 400 7th St. S.W., Washington D.C. 20590. Copies of the SAE Recommended Practice SAE J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests, are available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096. Copies may be inspected at the Office of the Secretary, Consumer Product Safety Commission, 4330 East-West Highway, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, or at the Office of the Federal Register, 800 N. Capitol Street NW, Room 700, Washington, DC.
(1) Draft ISO/DIS Standard 6220-1983 - Headforms for Use in the Testing of Protective Helmets.
(2) Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 218, Motorcycle Helmets.
(3) SAE Recommended Practice SAE J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests.
(2) Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 218, Motorcycle Helmets.
(3) SAE Recommended Practice SAE J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests.
(b) This incorporation by reference was approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51. Copies of the standards may be obtained as follows. Copies of the draft ISO/DIS Standard 6220-1983 are available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036. Copies of the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 218, Motorcycle Helmets, are available from the Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Office of Vehicle Safety Standards, 400 7th St. S.W., Washington D.C. 20590. Copies of the SAE Recommended Practice SAE J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests, are available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096. Copies may be inspected at the Office of the Secretary, Consumer Product Safety Commission, 4330 East-West Highway, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, or at the Office of the Federal Register, 800 N. Capitol Street NW, Room 700, Washington, DC.
§1203.4 Definitions
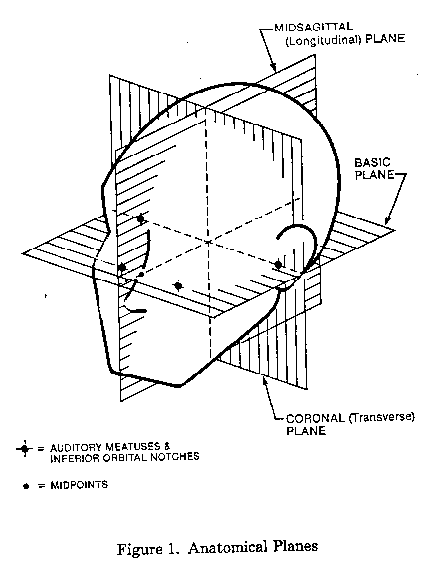
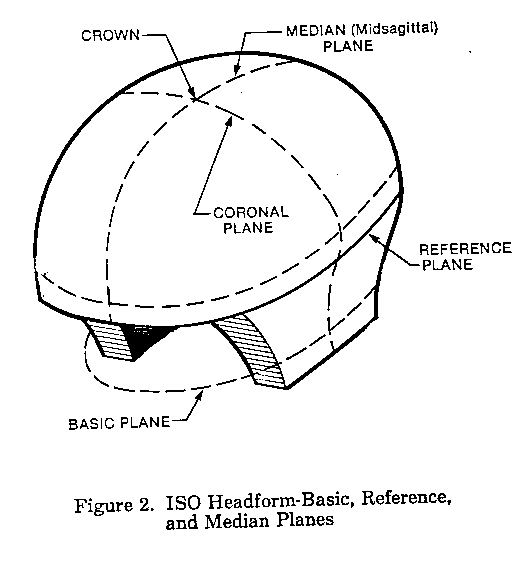
(a) Basic plane means an anatomical plane that includes the auditory meatuses (the external ear openings) and
the inferior orbital rims (the bottom edges of the eye sockets). The ISO headforms are marked with a plane
corresponding to this basic plane (see Figures 1 and 2 of this part).
(b) Bicycle helmet means any headgear that either is marketed as, or implied through marketing or promotion to be, a device intended to provide protection from head injuries while riding a bicycle. [Footnote 1]
==========Footnote==========(b) Bicycle helmet means any headgear that either is marketed as, or implied through marketing or promotion to be, a device intended to provide protection from head injuries while riding a bicycle. [Footnote 1]
[1] Helmets specifically marketed for exclusive use in a designated activity, such as skateboarding, rollerblading, baseball, roller hockey, etc., would be excluded from this definition because the specific focus of their marketing makes it unlikely that such helmets would be purchased for other than their stated use. However, a multi-purpose helmet -one marketed or represented as providing protection either during general use or in a variety of specific activities other than bicycling -would fall within the definition of bicycle helmet if a reasonable consumer could conclude, based on the helmet's marketing or representations, that bicycling is among the activities in which the helmet is intended to be used. In making this determination, the Commission will consider the types of specific activities, if any, for which the helmet is marketed, the similarity of the appearance, design, and construction of the helmet to other helmets marketed or recognized as bicycle helmets, and the presence, prominence, and clarity of any warnings, on the helmet or its packaging or promotional materials, against the use of the helmet as a bicycle helmet. A multi-purpose helmet marketed without specific reference to the activities in which the helmet is to be used will be presumed to be a bicycle helmet. The presence of warnings or disclaimers advising against the use of a multi-purpose helmet during bicycling is a relevant, but not necessarily controlling, factor in the determination of whether a multi-purpose helmet is a bicycle helmet.
======End of Footnote=======
(c) Comfort or fit padding means resilient lining material used to configure the helmet for a range of different head sizes.
(d) Coronal plane is an anatomical plane perpendicular to both the basic and midsagittal planes and containing the midpoint of a line connecting the right and left auditory meatuses. The ISO headforms are marked with a transverse plane corresponding to this coronal plane (see Figures 1 and 2 of this part).
(e) Field of vision is the angle of peripheral vision allowed by the helmet when positioned on the reference headform.
(f) Helmet positioning index ("HPI") is the vertical distance from the brow of the helmet to the reference plane, when placed on a reference headform. This vertical distance shall be specified by the manufacturer for each size of each model of the manufacturer's helmets, for the appropriate size of headform for each helmet, as described in § 1203.10.
(g) Midsagittal plane is an anatomical plane perpendicular to the basic plane and containing the midpoint of the line connecting the notches of the right and left inferior orbital ridges and the midpoint of the line connecting the superior rims of the right and left auditory meatuses. The ISO headforms are marked with a longitudinal plane corresponding to the midsagittal plane (see Figures 1 and 2 of this part).
(h) Modular elastomer programmer ("MEP") is a cylindrical pad, typically consisting of a polyurethane rubber, used as a consistent impact medium for the systems check procedure. The MEP shall be 152 mm (6 in) in diameter, and 25 mm (1 in) thick and shall have a durometer of 60 2 Shore A. The MEP shall be affixed to the top surface of a flat 6.35 mm (1/4 in) thick aluminum plate. See § 1203.17(b)(1).
(i) Preload ballast is a "bean bag" filled with lead shot that is placed on the helmet to secure its position on the headform. The mass of the preload ballast is 5 kg (11 lb).
(j) Projection is any part of the helmet, internal or external, that extends beyond the faired surface.
(k) Reference headform is a headform used as a measuring device and contoured in the same configuration as one of the test headforms A, E, J, M, and O defined in draft ISO DIS 6220-1983. The reference headform shall include surface markings corresponding to the basic, coronal, midsagittal, and reference planes (see Figures 1 and 2 of this part).
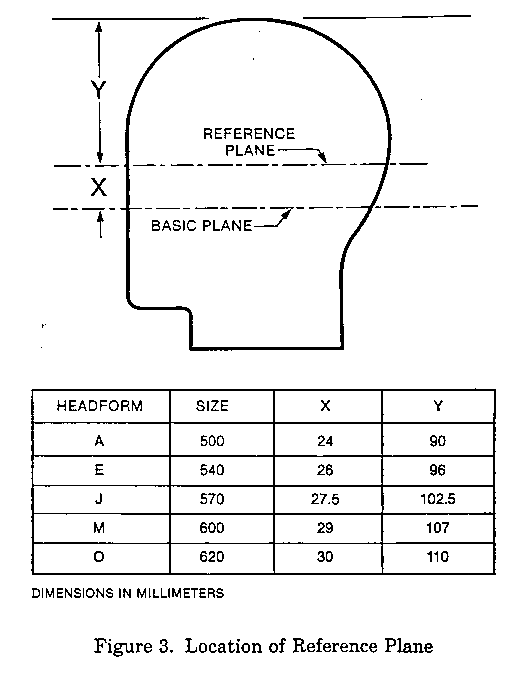
(l) Reference plane is a plane marked on the ISO headforms at a specified distance above and parallel to the basic plane (see Figure 3 of this part).
(m) Retention system is the complete assembly that secures the helmet in a stable position on the wearer's head.
(n) Shield means optional equipment for helmets that is used in place of goggles to protect the eyes.
(o) Spherical impactor is an impact fixture used in the instrument system check of § 1203.17 (b)(1) to test the impact-attenuation test equipment for precision and accuracy. The spherical impactor shall be a 146 mm (5.75 in) diameter aluminum sphere mounted on the ball-arm connector of the drop assembly. The total mass of the spherical-impactor drop assembly shall be 5.0 + 0.1 kg (11.0 + O. 22 lb).
(p) Test headform is a solid model in the shape of a human head of sizes A, E, J, M, and O as defined in draft ISO/DIS 6220-1983. Headforms used for the impact-attenuation test shall be constructed of low-resonance K-1A magnesium alloy. The test headforms shall include surface markings corresponding to the basic, coronal, midsagittal, and reference planes (see Figure 2 of this part).
(q) Test region is the area of the helmet, on and above a specified impact test line, that is subject to impact testing.
§ 1203.5 Construction requirements - projections.
Any unfaired projection extending more than 7 mm (0.28 in.) from the helmet's outer surface shall
break away or collapse when impacted with forces equivalent to those produced by the applicable impact-attenuation tests
in § 1203.17 of this standard. There shall be no fixture on the helmet's inner surface projecting more than 2 mm
into the helmet's interior.
§ 1203.6 Labeling and instructions.
(a) Labeling. Each helmet shall be marked with durable labeling so that the following information is legible and
easily visible to the user:
(b) Instructions. Each helmet shall have fitting and positioning instructions, including a graphic representation of proper positioning.
(1) Model designation.
(2) A warning to the user that no helmet can protect against all possible impacts and that serious injury or death could occur.
(3) A warning on both the helmet and the packaging that for maximum protection the helmet must be fitted and attached properly to the wearer's head in accordance with the manufacturer's fitting instructions.
(4) A warning to the user that the helmet may, after receiving an impact, be damaged to the point that it is no longer adequate to protect the head against further impacts, and that this damage may not be visible to the user. This label shall also state that a helmet that has sustained an impact should be returned to the manufacturer for inspection, or be destroyed and replaced.
(5) A warning to the user that the helmet can be damaged by contact with common substances (for example, certain solvents [ammonia], cleaners [bleach], etc.), and that this damage may not be visible to the user. This label shall state in generic terms some recommended cleaning agents and procedures (for example, wipe with mild soap and water), list the most common substances that damage the helmet, warn against contacting the helmet with these substances, and refer users to the instruction manual for more specific care and cleaning information.
(6) Signal word. The labels required by paragraphs (2) - (5) shall include the signal word "WARNING" at the beginning of each statement, unless two or more of the statements appear together on the same label. In that case, the signal word need only appear once, at the beginning of the warnings. The signal word "WARNING" shall be in all capital letters, bold print, and a type size equal to or greater than the other text on the label.
(2) A warning to the user that no helmet can protect against all possible impacts and that serious injury or death could occur.
(3) A warning on both the helmet and the packaging that for maximum protection the helmet must be fitted and attached properly to the wearer's head in accordance with the manufacturer's fitting instructions.
(4) A warning to the user that the helmet may, after receiving an impact, be damaged to the point that it is no longer adequate to protect the head against further impacts, and that this damage may not be visible to the user. This label shall also state that a helmet that has sustained an impact should be returned to the manufacturer for inspection, or be destroyed and replaced.
(5) A warning to the user that the helmet can be damaged by contact with common substances (for example, certain solvents [ammonia], cleaners [bleach], etc.), and that this damage may not be visible to the user. This label shall state in generic terms some recommended cleaning agents and procedures (for example, wipe with mild soap and water), list the most common substances that damage the helmet, warn against contacting the helmet with these substances, and refer users to the instruction manual for more specific care and cleaning information.
(6) Signal word. The labels required by paragraphs (2) - (5) shall include the signal word "WARNING" at the beginning of each statement, unless two or more of the statements appear together on the same label. In that case, the signal word need only appear once, at the beginning of the warnings. The signal word "WARNING" shall be in all capital letters, bold print, and a type size equal to or greater than the other text on the label.
(b) Instructions. Each helmet shall have fitting and positioning instructions, including a graphic representation of proper positioning.
§ 1203.7 Samples for testing.
(a) General. Helmets shall be tested in the condition in which they are offered for sale. To meet the standard,
the helmets must be able to pass all tests, both with and without any attachments that may be offered by the helmet's
manufacturer and with all possible combinations of such attachments.
(b) Number of samples. To test conformance to this standard, eight samples of each helmet size for each helmet model offered for sale are required.
(b) Number of samples. To test conformance to this standard, eight samples of each helmet size for each helmet model offered for sale are required.
§ 1203.8 Conditioning environments.
Helmets shall be conditioned to one of the following environments prior to testing in accordance with the test schedule
at § 1203.13. The barometric pressure in all conditioning environments shall be 75 to 110 kPa (22.2 to 32.6 in of
Hg). All test helmets shall be stabilized within the ambient condition for at least 4 hours prior to further conditioning
and testing. Storage or shipment within this ambient range satisfies this requirement.
(a) Ambient condition. The ambient condition of the test laboratory shall be within 17 degrees C to 27 degrees C (63 degrees F to 81 degrees F), and 20 to 80 degrees relative humidity. The ambient test helmet does not need further conditioning.
(b) Low temperature. The helmet shall be kept at a temperature of -17 degrees C to -13 degrees C (1 degrees F to 9 degrees F) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
(c) High temperature. The helmet shall be kept at a temperature of 47 degrees C to 53 degrees C (117 degrees F to 127 degrees F) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
(d) Water immersion. The helmet shall be fully immersed "crown" down in potable water at a temperature of 17 degrees C to 27 degrees C (63 degrees F to 81 degrees F) to a crown depth of 305 mm +/- 25 mm (12 in. +/- 1 in.) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
(a) Ambient condition. The ambient condition of the test laboratory shall be within 17 degrees C to 27 degrees C (63 degrees F to 81 degrees F), and 20 to 80 degrees relative humidity. The ambient test helmet does not need further conditioning.
(b) Low temperature. The helmet shall be kept at a temperature of -17 degrees C to -13 degrees C (1 degrees F to 9 degrees F) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
(c) High temperature. The helmet shall be kept at a temperature of 47 degrees C to 53 degrees C (117 degrees F to 127 degrees F) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
(d) Water immersion. The helmet shall be fully immersed "crown" down in potable water at a temperature of 17 degrees C to 27 degrees C (63 degrees F to 81 degrees F) to a crown depth of 305 mm +/- 25 mm (12 in. +/- 1 in.) for 4 to 24 hours prior to testing.
§ 1203.9 Test headforms.
The headforms used for testing shall be selected from sizes A, E, J, M, and O, as defined by DRAFT ISO/DIS 6220-1983, in
accordance with § 1203.10. Headforms used for impact testing shall be rigid and be constructed of low-resonance K-1A
magnesium alloy.
§ 1203.10 Selecting the test headform.
A helmet shall be tested on the smallest of the headforms appropriate for the helmet sample. A headform size is
appropriate for a helmet if all of the helmet's sizing pads are partially compressed when the helmet is equipped with its
thickest sizing pads and positioned correctly on the reference headform.
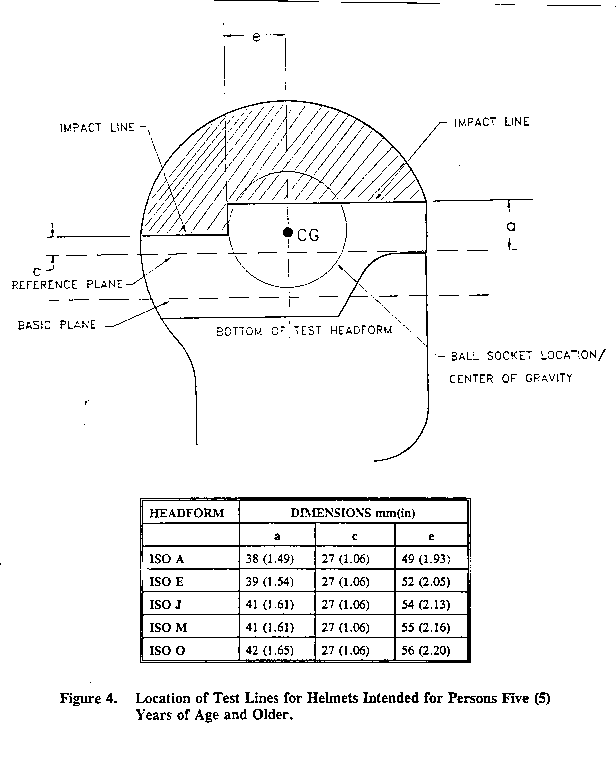
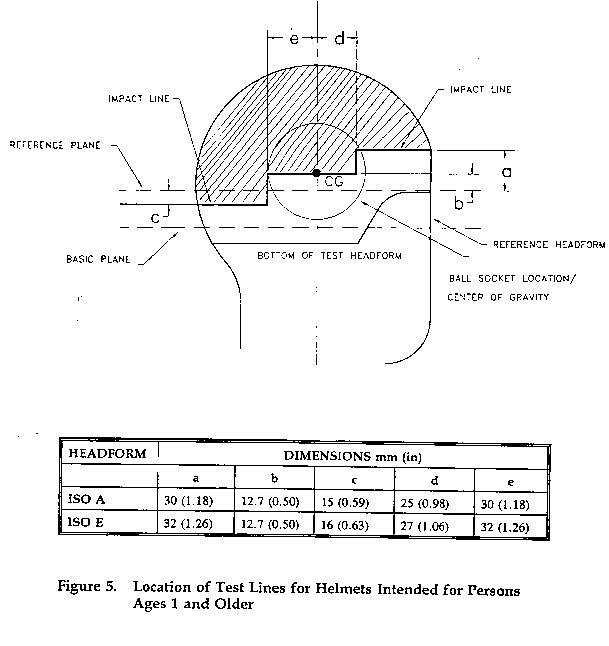
§ 1203.11 Marking the impact test line.
Prior to testing, the impact test line shall be determined for each helmet in the following manner.
(a) Position the helmet on the appropriate headform as specified by the manufacturer's helmet positioning index (HPI),
with the brow parallel to the basic plane. Place a 5-kg (11-lb) preload ballast on top of the helmet to set the comfort
or fit padding.
(b) Draw the impact test line on the outer surface of the helmet coinciding with the intersection of the surface of the helmet with the impact line planes defined from the reference headform as shown in
(c) The center of the impact sites shall be selected at any point on the helmet on or above the impact test line.
(b) Draw the impact test line on the outer surface of the helmet coinciding with the intersection of the surface of the helmet with the impact line planes defined from the reference headform as shown in
(1) Figure 4 of this part for helmets intended only for persons 5 years of age and older.
(2) Figure 5 of this part for helmets intended for persons age 1 and older.
(2) Figure 5 of this part for helmets intended for persons age 1 and older.
(c) The center of the impact sites shall be selected at any point on the helmet on or above the impact test line.
§ 1203.12 Test requirements.
(a) Peripheral vision. All bicycle helmets shall allow unobstructed vision through a minimum
of 105 degrees to the left and right sides of the midsagittal plane when measured in accordance with § 1203.14 of this
standard.
(b) Positional stability. No bicycle helmet shall come off of the test headform when tested in accordance with § 1203.15 of this standard.
(c) Dynamic strength of retention system. All bicycle helmets shall have a retention system that will remain intact without elongating more than 30 mm (1.2 in.) when tested in accordance with § 1203.16 of this standard.
(d) Impact attenuation criteria.
(b) Positional stability. No bicycle helmet shall come off of the test headform when tested in accordance with § 1203.15 of this standard.
(c) Dynamic strength of retention system. All bicycle helmets shall have a retention system that will remain intact without elongating more than 30 mm (1.2 in.) when tested in accordance with § 1203.16 of this standard.
(d) Impact attenuation criteria.
(1) General. A helmet fails the impact attenuation performance test of this standard if a failure under paragraph
(d)(2) of this section can be induced under any combination of impact site, anvil type, anvil impact order, or
conditioning environment permissible under the standard, either with or without any attachments, or combinations of
attachments, that are provided with the helmet. Thus, the Commission will test for a "worst case" combination
of test parameters. What constitutes a worst case may vary, depending on the particular helmet involved.
(2) Peak acceleration. The peak acceleration of any impact shall not exceed 300 g when the helmet is tested in accordance with Sec. 1203.17 of this standard.
(2) Peak acceleration. The peak acceleration of any impact shall not exceed 300 g when the helmet is tested in accordance with Sec. 1203.17 of this standard.
§ 1203.13 Test schedule.
(a) Helmet sample 1 of the set of eight helmets, as designated in Table 1203.13, shall be tested for peripheral vision in
accordance with § 1203.14 of this standard.
(b) Helmet samples 1 through 8, as designated in Table 1203.13, shall be conditioned in the ambient, high temperature, low temperature, and water immersion environments as follows: helmets 1 and 5 - ambient; helmets 2 and 7 - high temperature; helmets 3 and 6 - low temperature; and helmets 4 and 8 - water immersion.
(c) Testing must begin within 2 minutes after the helmet is removed from the conditioning environment. The helmet shall be returned to the conditioning environment within 3 minutes after it was removed, and shall remain in the conditioning environment for a minimum of 2 minutes before testing is resumed. If the helmet is out of the conditioning environment beyond 3 minutes, testing shall not resume until the helmet has been reconditioned for a period equal to at least 5 minutes for each minute the helmet was out of the conditioning environment beyond the first 3 minutes, or for 4 hours, (whichever reconditioning time is shorter) before testing is resumed.
(d) Prior to being tested for impact attenuation, helmets 1-4 (conditioned in ambient, high temperature, low temperature, and water immersion environments, respectively) shall be tested in accordance with the dynamic retention system strength test at § 1203.16. Helmets 1-4 shall then be tested in accordance with the impact attenuation tests on the flat and hemispherical anvils in accordance with the procedure at § 1203.17. Helmet 5 (ambient-conditioned) shall be tested in accordance with the positional stability tests at § 1203.15 prior to impact testing. Helmets 5-8 shall then be tested in accordance with the impact attenuation tests on the curbstone anvil in accordance with § 1203.17. Table 1203.13 summarizes the test schedule.
(b) Helmet samples 1 through 8, as designated in Table 1203.13, shall be conditioned in the ambient, high temperature, low temperature, and water immersion environments as follows: helmets 1 and 5 - ambient; helmets 2 and 7 - high temperature; helmets 3 and 6 - low temperature; and helmets 4 and 8 - water immersion.
(c) Testing must begin within 2 minutes after the helmet is removed from the conditioning environment. The helmet shall be returned to the conditioning environment within 3 minutes after it was removed, and shall remain in the conditioning environment for a minimum of 2 minutes before testing is resumed. If the helmet is out of the conditioning environment beyond 3 minutes, testing shall not resume until the helmet has been reconditioned for a period equal to at least 5 minutes for each minute the helmet was out of the conditioning environment beyond the first 3 minutes, or for 4 hours, (whichever reconditioning time is shorter) before testing is resumed.
(d) Prior to being tested for impact attenuation, helmets 1-4 (conditioned in ambient, high temperature, low temperature, and water immersion environments, respectively) shall be tested in accordance with the dynamic retention system strength test at § 1203.16. Helmets 1-4 shall then be tested in accordance with the impact attenuation tests on the flat and hemispherical anvils in accordance with the procedure at § 1203.17. Helmet 5 (ambient-conditioned) shall be tested in accordance with the positional stability tests at § 1203.15 prior to impact testing. Helmets 5-8 shall then be tested in accordance with the impact attenuation tests on the curbstone anvil in accordance with § 1203.17. Table 1203.13 summarizes the test schedule.
TABLE 1203.13 - TEST SCHEDULE
§1203.14 §1203.15 §1203.16 §1203.17
Peripheral Positional Retention Impact Tests
Vision Stability System No. of
Strength Anvil Impacts
Helmet 1 X X X Flat 2
Ambient X Hemi 2
Helmet 2 X X Flat 2
High X Hemi 2
Temperature
Helmet 3 X X Flat 2
Low X Hemi 2
Temperature
Helmet 4 X X Flat 2
Water X Hemi 2
Immersion
Helmet 5 X X Curb 1
Ambient
Helmet 6 X Curb 1
Low
Temperature
Helmet 7 X Curb 1
High
Temperature
Helmet 8 X Curb 1
Water
Immersion
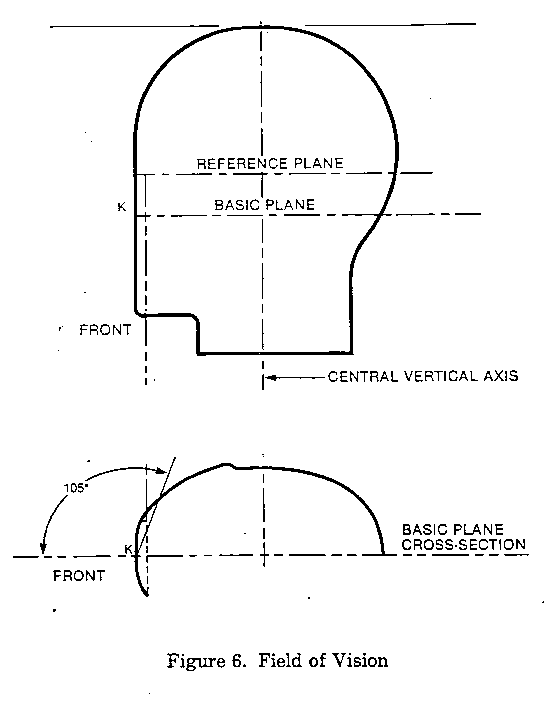
§ 1203.14 Peripheral vision test.
Position the helmet on a reference headform in accordance with the HPI and place a 5-kg (11-lb) preload ballast on top of
the helmet to set the comfort or fit padding. (Note: Peripheral vision clearance may be determined when the helmet is
positioned for marking the test lines.) Peripheral vision is measured horizontally from each side of the midsagittal
plane around the point K (see Figure 6 of this part). Point K is located on the front surface of the reference headform
at the intersection of the basic and midsagittal planes. The vision shall not be obstructed within 105 degrees from point
K on each side of the midsagittal plane.
§ 1203.15 Positional stability test (roll-off resistance).
(a) Test equipment.
(b) Test procedure.
(1) Headforms. The test headforms shall comply with the dimensions of the full chin ISO reference headforms
sizes A, E, J, M, and O.
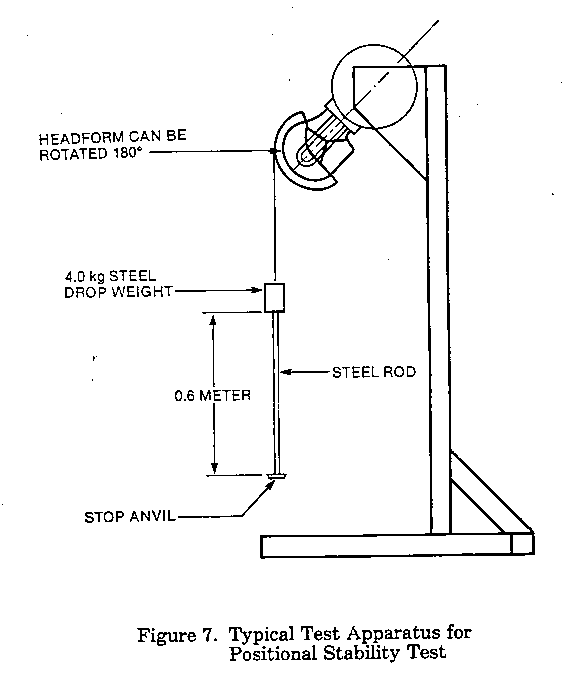
(2) Test fixture. The headform shall be secured in a test fixture with the headform's vertical axis pointing downward and 45 degrees to the direction of gravity (see Figure 7 of this part). The test fixture shall permit rotation of the headform about its vertical axis and include means to lock the headform in the face up and face down positions.
(3) Dynamic impact apparatus. A dynamic impact apparatus shall be used to apply a shock load to a helmet secured to the test headform. The dynamic impact apparatus shall allow a 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to slide in a guided free fall to impact a rigid stop anvil (see Figure 7 of this part). The entire mass of the dynamic impact assembly, including the drop weight, shall be no more than 5 kg (11 lb).
(4) Strap or cable. A hook and flexible strap or cable shall be used to connect the dynamic impact apparatus to the helmet. The strap or cable shall be of a material having an elongation of no more than 5 mm (0.20 in.) per 300 mm (11.8 in.) when loaded with a 22-kg (48.5 lb) weight in a free hanging position.
(2) Test fixture. The headform shall be secured in a test fixture with the headform's vertical axis pointing downward and 45 degrees to the direction of gravity (see Figure 7 of this part). The test fixture shall permit rotation of the headform about its vertical axis and include means to lock the headform in the face up and face down positions.
(3) Dynamic impact apparatus. A dynamic impact apparatus shall be used to apply a shock load to a helmet secured to the test headform. The dynamic impact apparatus shall allow a 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to slide in a guided free fall to impact a rigid stop anvil (see Figure 7 of this part). The entire mass of the dynamic impact assembly, including the drop weight, shall be no more than 5 kg (11 lb).
(4) Strap or cable. A hook and flexible strap or cable shall be used to connect the dynamic impact apparatus to the helmet. The strap or cable shall be of a material having an elongation of no more than 5 mm (0.20 in.) per 300 mm (11.8 in.) when loaded with a 22-kg (48.5 lb) weight in a free hanging position.
(b) Test procedure.
(1) Orient the headform so that its face is down, and lock it in that orientation.
(2) Place the helmet on the appropriate size full chin headform in accordance with the HPI and fasten the retention system in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Adjust the straps to remove any slack.
(3) Suspend the dynamic impact system from the helmet by positioning the flexible strap over the helmet along the midsagittal plane and attaching the hook over the edge of the helmet as shown in Figure 7 of this part.
(4) Raise the drop weight to a height of 0.6 m (2 ft) from the stop anvil and release it, so that it impacts the stop anvil.
(5) The test shall be repeated with the headform's face pointing upwards, so that the helmet is pulled from front to rear.
(2) Place the helmet on the appropriate size full chin headform in accordance with the HPI and fasten the retention system in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Adjust the straps to remove any slack.
(3) Suspend the dynamic impact system from the helmet by positioning the flexible strap over the helmet along the midsagittal plane and attaching the hook over the edge of the helmet as shown in Figure 7 of this part.
(4) Raise the drop weight to a height of 0.6 m (2 ft) from the stop anvil and release it, so that it impacts the stop anvil.
(5) The test shall be repeated with the headform's face pointing upwards, so that the helmet is pulled from front to rear.
§ 1203.16 Dynamic strength of retention system test.
(a) Test equipment.
(1) ISO headforms without the lower chin portion shall be used.
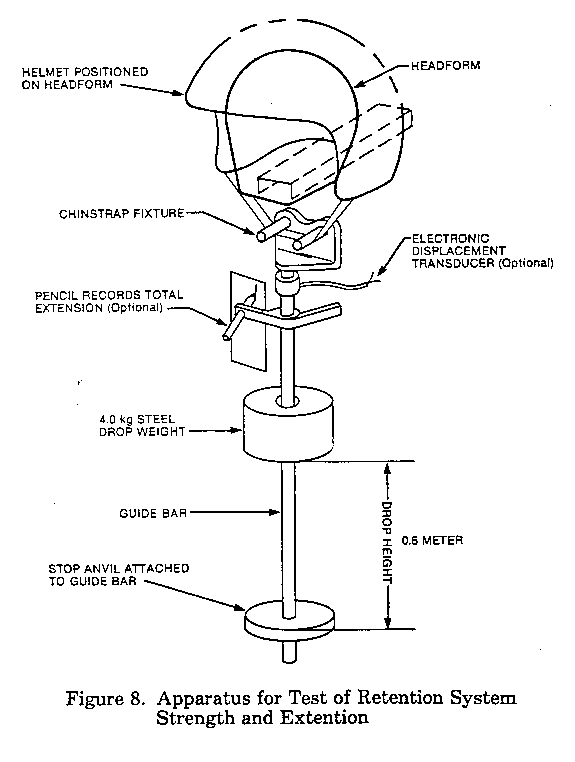
(2) The retention system strength test equipment shall consist of a dynamic impact apparatus that allows a 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to slide in a guided free fall to impact a rigid stop anvil (see Figure 8 of this part). Two cylindrical rollers that spin freely, with a diameter of 12.5 +/- 0.5 mm (0.49 in. +/- 0.02 in.) and a center-to-center distance of 76.0 +/- 1 mm (3.0 +/- 0.04 in.), shall make up a stirrup that represents the bone structure of the lower jaw. The entire dynamic test apparatus hangs freely on the retention system. The entire mass of the support assembly, including the 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight, shall be 11 kg 0.5 kg (24.2 lb +/- 1.1 lb).
(b) Test procedure.
(2) The retention system strength test equipment shall consist of a dynamic impact apparatus that allows a 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to slide in a guided free fall to impact a rigid stop anvil (see Figure 8 of this part). Two cylindrical rollers that spin freely, with a diameter of 12.5 +/- 0.5 mm (0.49 in. +/- 0.02 in.) and a center-to-center distance of 76.0 +/- 1 mm (3.0 +/- 0.04 in.), shall make up a stirrup that represents the bone structure of the lower jaw. The entire dynamic test apparatus hangs freely on the retention system. The entire mass of the support assembly, including the 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight, shall be 11 kg 0.5 kg (24.2 lb +/- 1.1 lb).
(1) Place the helmet on the appropriate size headform on the test device according to the HPI. Fasten the strap of the
retention system under the stirrup.
(2) Mark the pre-test position of the retention system, with the entire dynamic test apparatus hanging freely on the retention system.
(3) Raise the 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to a height of 0.6 m (2 ft) from the stop anvil and release it, so that it impacts the stop anvil.
(4) Record the maximum elongation of the retention system during the impact. A marker system or a displacement transducer, as shown in Figure 8 of this part, are two methods of measuring the elongation.
(2) Mark the pre-test position of the retention system, with the entire dynamic test apparatus hanging freely on the retention system.
(3) Raise the 4-kg (8.8-lb) drop weight to a height of 0.6 m (2 ft) from the stop anvil and release it, so that it impacts the stop anvil.
(4) Record the maximum elongation of the retention system during the impact. A marker system or a displacement transducer, as shown in Figure 8 of this part, are two methods of measuring the elongation.
§ 1203.17 Impact attenuation test.
(a) Impact test instruments and equipment.
(b) Test Procedure.
(1) Measurement of impact attenuation. Impact attenuation is determined by measuring the acceleration of the
test headform during impact. Acceleration is measured with a uniaxial accelerometer that is capable of withstanding a
shock of a least 1000 g. The helmet is secured onto the headform and dropped in a guided free fall, using a monorail or
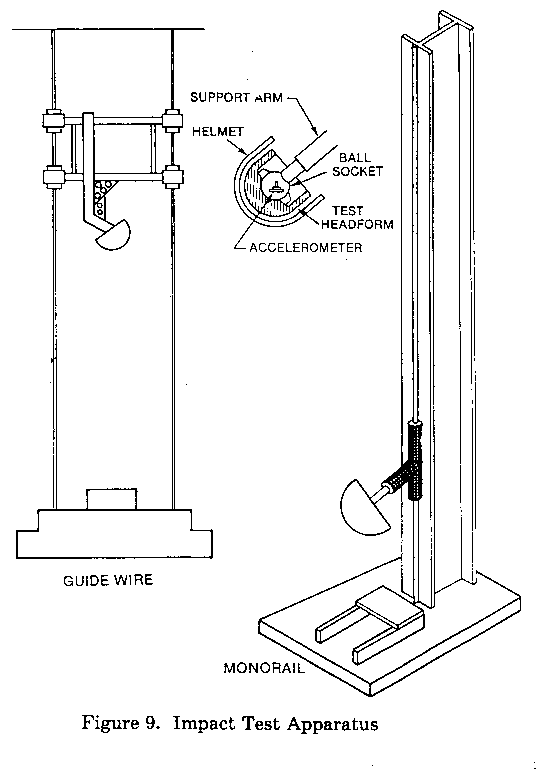
guidewire test apparatus (see Figure 9 of this part), onto an anvil fixed to a rigid base. The center of the anvil
shall be aligned with the center vertical axis of the accelerometer. The base shall consist of a solid mass of at least
135 kg (298 lb), the upper surface of which shall consist of a steel plate at least 12 mm (0.47 in.) thick and having a
surface area of at least 0.10 sq. m (1.08 sq. ft.).
(2) Accelerometer. A uniaxial accelerometer shall be mounted at the center of gravity of the test headform, with the sensitive axis aligned within 5 degrees of vertical when the test headform is in the impact position. The acceleration data channel and filtering shall comply with SAE Recommended Practice J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests, Requirements for Channel Class 1000.
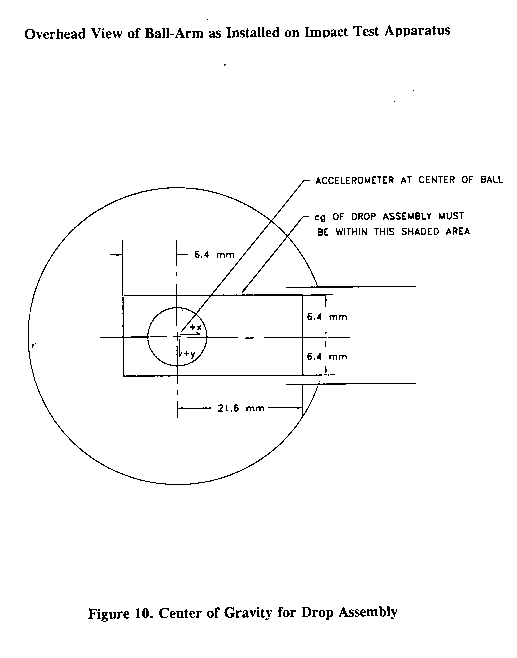
(3) Headform and drop assembly-centers of gravity. The center of gravity of the test headform shall be at the center of the mounting ball on the support assembly and within an inverted cone having its axis vertical and a 10-degree included angle with the vertex at the point of impact. The location of the center of gravity of the drop assembly (combined test headform and support assembly) must meet FMVSS 218 S7.1.8. The center of gravity of the drop assembly shall lie within the rectangular volume bounded by x = -6.4 mm (-0.25 in.), x = 21.6 mm (0.85 in), y = 6.4 mm (0.25 in.), and y = -6.4 mm (-0.25 in), with the origin located at the center of gravity of the test headform. The origin of the coordinate axes is at the center of the mounting ball on the support assembly. The rectangular volume has no boundary along the z-axis. The positive z-axis is downward. The x-y-z axes are mutually perpendicular and have positive or negative designations as shown in Figure 10 of this part. Figure 10 shows an overhead view of the x-y boundary of the drop assembly center of gravity.
(4) Drop assembly. The combined mass of the drop assembly, which consists of instrumented test headform and support assembly (excluding the test helmet), shall be 5.0 +/- 0.1 kg (11.00 +/- 0.22 lb).
(5) Impact anvils. Impact tests shall be performed against the three different solid (i.e., without internal cavities) steel anvils described below.
(2) Accelerometer. A uniaxial accelerometer shall be mounted at the center of gravity of the test headform, with the sensitive axis aligned within 5 degrees of vertical when the test headform is in the impact position. The acceleration data channel and filtering shall comply with SAE Recommended Practice J211 OCT88, Instrumentation for Impact Tests, Requirements for Channel Class 1000.
(3) Headform and drop assembly-centers of gravity. The center of gravity of the test headform shall be at the center of the mounting ball on the support assembly and within an inverted cone having its axis vertical and a 10-degree included angle with the vertex at the point of impact. The location of the center of gravity of the drop assembly (combined test headform and support assembly) must meet FMVSS 218 S7.1.8. The center of gravity of the drop assembly shall lie within the rectangular volume bounded by x = -6.4 mm (-0.25 in.), x = 21.6 mm (0.85 in), y = 6.4 mm (0.25 in.), and y = -6.4 mm (-0.25 in), with the origin located at the center of gravity of the test headform. The origin of the coordinate axes is at the center of the mounting ball on the support assembly. The rectangular volume has no boundary along the z-axis. The positive z-axis is downward. The x-y-z axes are mutually perpendicular and have positive or negative designations as shown in Figure 10 of this part. Figure 10 shows an overhead view of the x-y boundary of the drop assembly center of gravity.
(4) Drop assembly. The combined mass of the drop assembly, which consists of instrumented test headform and support assembly (excluding the test helmet), shall be 5.0 +/- 0.1 kg (11.00 +/- 0.22 lb).
(5) Impact anvils. Impact tests shall be performed against the three different solid (i.e., without internal cavities) steel anvils described below.
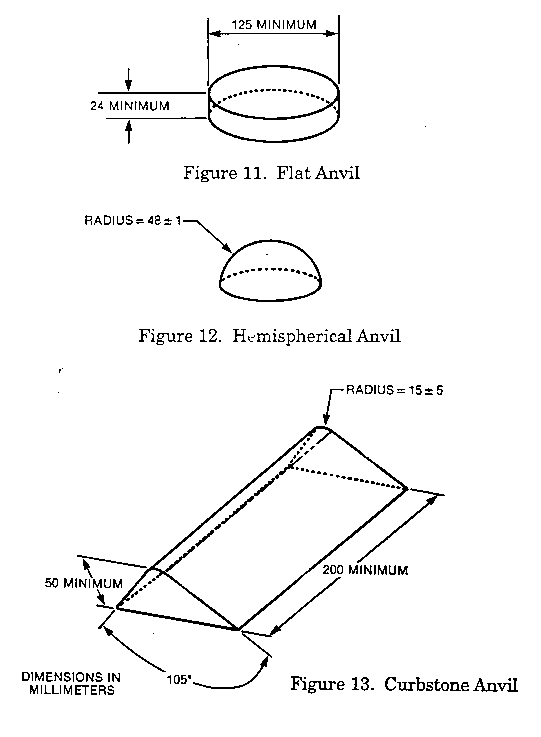
(i) Flat Anvil. The flat anvil shall have a flat surface with an impact face having a minimum diameter of 125
mm (4.92 in.). It shall be at least 24 mm (0.94 in.) thick (see Figure 11 of this part).
(ii) Hemispherical anvil. The hemispherical anvil shall have a hemispherical impact surface with a radius of 48 +/- 1 mm (1.89 +/- 0.04 in.) (see Figure 12 of this part).
(iii) Curbstone anvil. The curbstone anvil shall have two flat faces making an angle of 105 degrees and meeting along a striking edge having a radius of 15 mm +/- 0.5 mm (0.59 +/- 0.02 in.). The height of the curbstone anvil shall not be less than 50 mm (1.97 in.), and the length shall not be less than 200 mm (7.87 in.) (see Figure 13 of this part).
(ii) Hemispherical anvil. The hemispherical anvil shall have a hemispherical impact surface with a radius of 48 +/- 1 mm (1.89 +/- 0.04 in.) (see Figure 12 of this part).
(iii) Curbstone anvil. The curbstone anvil shall have two flat faces making an angle of 105 degrees and meeting along a striking edge having a radius of 15 mm +/- 0.5 mm (0.59 +/- 0.02 in.). The height of the curbstone anvil shall not be less than 50 mm (1.97 in.), and the length shall not be less than 200 mm (7.87 in.) (see Figure 13 of this part).
(b) Test Procedure.
(1) Instrument system check (precision and accuracy). The impact-attenuation test instrumentation shall be
checked before and after each series of tests (at least at the beginning and end of each test day) by dropping a
spherical impactor onto an elastomeric test medium (MEP). The spherical impactor shall be a 146 mm (5.75 in) diameter
aluminum sphere that is mounted on the ball-arm connector of the drop assembly. The total mass of the
spherical-impactor drop assembly shall be 5.0 +/- 0.1 kg (11.0 +/- 0.22 lb). The MEP shall be 152 mm (6 in) in diameter
and 25 mm (1 in) thick, and shall have a durometer of 60 +/- 2 Shore A. The MEP shall be affixed to the top surface of
a flat 6.35 mm (1/4 in) thick aluminum plate. The geometric center of the MEP pad shall be aligned with the center
vertical axis of the accelerometer (see § 1203.17(a)(2)). The impactor shall be dropped onto the MEP at an impact
velocity of 5.44 m/s +/- 2 per cent. (Typically, this requires a minimum drop height of 1.50 meters (4.9 ft) plus a
height adjustment to account for friction losses.) Six impacts, at intervals of 75 +/- 15 seconds, shall be performed
at the beginning and end of the test series (at a minimum at the beginning and end of each test day). The first three
of six impacts shall be considered warm-up drops, and their impact values shall be discarded from the series. The
second three impacts shall be recorded. All recorded impacts shall fall within the range of 380 g to 425 g. In
addition, the difference between the high and low values of the three recorded impacts shall not be greater than 20
g.
(2) Impact sites. Each of helmets 1 through 4 (one helmet for each conditioning environment) shall impact at four different sites, with two impacts on the flat anvil and two impacts on the hemispherical anvil. The center of any impact may be anywhere on or above the test line, provided it is at least 120 mm (4.72 in), measured on the surface of the helmet, from any prior impact center. Each of helmets 5 through 8 (one helmet for each conditioning environment) shall impact at one site on the curbstone anvil. The center of the curbstone impacts may be on or anywhere above the test line. The curbstone anvil may be placed in any orientation as long as the center of the anvil is aligned with the axis of the accelerometer. As noted in § 1203.12(d)(1), impact sites, the order of anvil use (flat and hemispherical), and curbstone anvil sites and orientation shall be chosen by the test personnel to provide the most severe test for the helmet. Rivets and other mechanical fasteners, vents, and any other helmet feature within the test region are valid test sites.
(3) Impact velocity. The helmet shall be dropped onto the flat anvil with an impact velocity of 6.2 m/s +/- 3 per cent (20.34 ft/s +/- 3 per cent). (Typically, this requires a minimum drop height of 2 meters (6.56 ft), plus a height adjustment to account for friction losses.) The helmet shall be dropped onto the hemispherical and curbstone anvils with an impact velocity of 4.8 m/s plus or minus 3 per cent (15.75 ft/s plus or minus 3 per cent). (Typically, this requires a minimum drop height of 1.2 meters (3.94 ft), plus a height adjustment to account for friction losses.) The impact velocity shall be measured during the last 40 mm (1.57 in) of free-fall for each test.
(4) Helmet position. Prior to each test, the helmet shall be positioned on the test headform in accordance with the HPI. The helmet shall be secured so that it does not shift position prior to impact. The helmet retention system shall be secured in a manner that does not interfere with free-fall or impact.
(5) Data. Record the maximum acceleration in g's during impact. See Subpart C, § 1203 .41 (b).
(2) Impact sites. Each of helmets 1 through 4 (one helmet for each conditioning environment) shall impact at four different sites, with two impacts on the flat anvil and two impacts on the hemispherical anvil. The center of any impact may be anywhere on or above the test line, provided it is at least 120 mm (4.72 in), measured on the surface of the helmet, from any prior impact center. Each of helmets 5 through 8 (one helmet for each conditioning environment) shall impact at one site on the curbstone anvil. The center of the curbstone impacts may be on or anywhere above the test line. The curbstone anvil may be placed in any orientation as long as the center of the anvil is aligned with the axis of the accelerometer. As noted in § 1203.12(d)(1), impact sites, the order of anvil use (flat and hemispherical), and curbstone anvil sites and orientation shall be chosen by the test personnel to provide the most severe test for the helmet. Rivets and other mechanical fasteners, vents, and any other helmet feature within the test region are valid test sites.
(3) Impact velocity. The helmet shall be dropped onto the flat anvil with an impact velocity of 6.2 m/s +/- 3 per cent (20.34 ft/s +/- 3 per cent). (Typically, this requires a minimum drop height of 2 meters (6.56 ft), plus a height adjustment to account for friction losses.) The helmet shall be dropped onto the hemispherical and curbstone anvils with an impact velocity of 4.8 m/s plus or minus 3 per cent (15.75 ft/s plus or minus 3 per cent). (Typically, this requires a minimum drop height of 1.2 meters (3.94 ft), plus a height adjustment to account for friction losses.) The impact velocity shall be measured during the last 40 mm (1.57 in) of free-fall for each test.
(4) Helmet position. Prior to each test, the helmet shall be positioned on the test headform in accordance with the HPI. The helmet shall be secured so that it does not shift position prior to impact. The helmet retention system shall be secured in a manner that does not interfere with free-fall or impact.
(5) Data. Record the maximum acceleration in g's during impact. See Subpart C, § 1203 .41 (b).
Subpart B - - Certification
§ 1203.30 Purpose, basis, and scope.
(a) Purpose. The purpose of this subpart is to establish requirements that manufacturers and importers of
bicycle helmets subject to the Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets (Subpart A of this Part 1203) shall issue
certificates of compliance in the form specified.
(b) Basis. Section 14(a)(1) of the Consumer Product Safety Act (CPSA), 15 U.S.C. 2063(a)(1), requires every manufacturer (including importers) and private labeler of a product which is subject to a consumer product safety standard to issue a certificate that the product conforms to the applicable standard. Section 14(a)(1) further requires that the certificate be based either on a test of each product or on a "reasonable testing program." The Commission may, by rule, designate one or more of the manufacturers and private labelers as the persons who shall issue the required certificate. 15 U.S.C. 2063(a)(2).
(c) Scope. The provisions of this subpart apply to all bicycle helmets that are subject to the requirements of the Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets, Subpart A of this Part 1203.
(b) Basis. Section 14(a)(1) of the Consumer Product Safety Act (CPSA), 15 U.S.C. 2063(a)(1), requires every manufacturer (including importers) and private labeler of a product which is subject to a consumer product safety standard to issue a certificate that the product conforms to the applicable standard. Section 14(a)(1) further requires that the certificate be based either on a test of each product or on a "reasonable testing program." The Commission may, by rule, designate one or more of the manufacturers and private labelers as the persons who shall issue the required certificate. 15 U.S.C. 2063(a)(2).
(c) Scope. The provisions of this subpart apply to all bicycle helmets that are subject to the requirements of the Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets, Subpart A of this Part 1203.
§ 1203.31 Effective date.
All bicycle helmets manufactured on or after [insert date that is 1 year plus 1 day after publication] must meet the
standard and must be certified as complying with the standard in accordance with this Subpart B.
§ 1203.32 Definitions.
The following definitions shall apply to this subpart:
(a) Foreign manufacturer means an entity that manufactured a bicycle helmet outside the United States, as
defined in 15 2052(a)(10) and (14).
(b) Manufacturer means the entity that either manufactured a helmet in the United States or imported a helmet manufactured outside the United States.
(c) Private labeler means an owner of a brand or trademark that is used on a bicycle helmet subject to the standard and that is not the brand or trademark of the manufacturer of the bicycle helmet, provided the owner of the brand or trademark caused, authorized, or approved its use.
(d) Production lot means a quantity of bicycle helmets from which certain bicycle helmets are selected for testing prior to certifying the lot. All bicycle helmets in a lot must be essentially identical in those design, construction, and material features that relate to the ability of a bicycle helmet to comply with the standard.
(e) Reasonable testing program means any tests which are identical or equivalent to, or more stringent than, the tests defined in the standard and which are performed on one or more bicycle helmets selected from the production lot to determine whether there is reasonable assurance that all of the bicycle helmets in that lot comply with the requirements of the standard.
(b) Manufacturer means the entity that either manufactured a helmet in the United States or imported a helmet manufactured outside the United States.
(c) Private labeler means an owner of a brand or trademark that is used on a bicycle helmet subject to the standard and that is not the brand or trademark of the manufacturer of the bicycle helmet, provided the owner of the brand or trademark caused, authorized, or approved its use.
(d) Production lot means a quantity of bicycle helmets from which certain bicycle helmets are selected for testing prior to certifying the lot. All bicycle helmets in a lot must be essentially identical in those design, construction, and material features that relate to the ability of a bicycle helmet to comply with the standard.
(e) Reasonable testing program means any tests which are identical or equivalent to, or more stringent than, the tests defined in the standard and which are performed on one or more bicycle helmets selected from the production lot to determine whether there is reasonable assurance that all of the bicycle helmets in that lot comply with the requirements of the standard.
§ 1203.33 Certification testing.
(a) General. Manufacturers, as defined in § 1203.32(b) to include importers, shall
conduct a reasonable testing program to demonstrate that their bicycle helmets comply with the requirements of the
standard.
(b) Reasonable testing program. This paragraph provides guidance for establishing a reasonable testing program.
(b) Reasonable testing program. This paragraph provides guidance for establishing a reasonable testing program.
(1) Within the requirements set forth below, manufacturers and importers may define their own reasonable testing
programs. Reasonable testing programs may, at the option of manufacturers and importers, be conducted by an independent
third party qualified to perform such testing programs. However, manufacturers and importers are responsible for ensuring
compliance with all requirements of this standard.
(2) As part of the reasonable testing program, the bicycle helmets shall be divided into production lots, and sample bicycle helmets from each production lot shall be tested. Whenever there is a change in parts, suppliers of parts, or production methods, and the change could affect the ability of the bicycle helmet to comply with the requirements of the standard, the manufacturer shall establish a new production lot for testing.
(3) The Commission will test for compliance with the standard by using the standard's test procedures. However, a reasonable testing program need not be identical to the tests prescribed in the standard.
(4) If the reasonable testing program shows that a bicycle helmet may not comply with one or more requirements of the standard, no bicycle helmet in the production lot can be certified as complying until sufficient actions are taken that it is reasonably likely that no noncomplying bicycle helmets remain in the production lot. All identified noncomplying helmets in the lot must be destroyed or altered by repair, redesign, or use of a different material or component, to the extent necessary to make them conform to the standard.
(5) The sale or offering for sale of a bicycle helmet that does not comply with the standard is a prohibited act and a violation of § l9 (a) of the CPSA (15 U.S.C. 2068(a)), regardless of whether the bicycle helmet has been validly certified.
(2) As part of the reasonable testing program, the bicycle helmets shall be divided into production lots, and sample bicycle helmets from each production lot shall be tested. Whenever there is a change in parts, suppliers of parts, or production methods, and the change could affect the ability of the bicycle helmet to comply with the requirements of the standard, the manufacturer shall establish a new production lot for testing.
(3) The Commission will test for compliance with the standard by using the standard's test procedures. However, a reasonable testing program need not be identical to the tests prescribed in the standard.
(4) If the reasonable testing program shows that a bicycle helmet may not comply with one or more requirements of the standard, no bicycle helmet in the production lot can be certified as complying until sufficient actions are taken that it is reasonably likely that no noncomplying bicycle helmets remain in the production lot. All identified noncomplying helmets in the lot must be destroyed or altered by repair, redesign, or use of a different material or component, to the extent necessary to make them conform to the standard.
(5) The sale or offering for sale of a bicycle helmet that does not comply with the standard is a prohibited act and a violation of § l9 (a) of the CPSA (15 U.S.C. 2068(a)), regardless of whether the bicycle helmet has been validly certified.
§ 1203.34 Product certification and labeling by manufacturers (including importers).
(a) Form of permanent label of certification. Manufacturers, as defined in § 1203.32(a), shall issue
certificates of compliance for bicycle helmets manufactured after [insert date that is 1 year after publication] in the
form of a durable, legible, and readily visible label meeting the requirements of this section. This label is the
helmet's certificate of compliance, as that term is used in § 14 of the CPSA, 15 U.S.C. 2063.
(b) Contents of certification label. The certification labels required by this section shall contain the following:
(c) Coding.
(e) Additional provisions for importers.
(b) Contents of certification label. The certification labels required by this section shall contain the following:
(1) The statement "Complies with CPSC Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets for Persons Age 5 and Older" or
"Complies with CPSC Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets for Persons Age 1 and older (Extended Head
Coverage)", as appropriate; this label may spell out "U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission" instead
of "CPSC";
(2) The name of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or the name of a private labeler;
(3) The address of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or, if the name of a private labeler is on the label, the address of the private labeler;
(4) The name and address of the foreign manufacturer, if the helmet was manufactured outside the United States;
(5) The telephone number of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or, if the name of a private labeler is on the label, the telephone number of the private labeler;
(6) An identification of the production lot;
and
(7) The uncoded month and year the product was manufactured.
(2) The name of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or the name of a private labeler;
(3) The address of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or, if the name of a private labeler is on the label, the address of the private labeler;
(4) The name and address of the foreign manufacturer, if the helmet was manufactured outside the United States;
(5) The telephone number of the U.S. manufacturer or importer responsible for issuing the certificate or, if the name of a private labeler is on the label, the telephone number of the private labeler;
(6) An identification of the production lot;
and
(7) The uncoded month and year the product was manufactured.
(c) Coding.
(1) The information required by paragraphs (b)(4) and (b)(6) of this section, and the information referred to in
paragraph (c)(2) of this section, may be in code, provided:
(d) Placement of the label (s). The information required by paragraphs (b)(2), (b)(3), and (b)(5) must be on
one label. The other required information may be on separate labels. The label(s) required by this section must be
affixed to the bicycle helmet. If the label(s) are not immediately visible to the ultimate purchaser of the bicycle
helmet prior to purchase because of packaging or other marketing practices, a second label is required. That label shall
state, as appropriate, "Complies with CPSC Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets for Persons Age 5 and Older", or
"Complies with CPSC Safety Standard for Bicycle Helmets for Persons Age 1 and Older (Extended Head Coverage)".
The label shall be legible, readily visible, and placed on the main display panel of the packaging or, if the packaging
is not visible before purchase (e.g., catalog sales), on the promotional material used with the sale of the bicycle
helmet. This label may spell out "U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission" instead of "CPSC."
(i) the person or firm issuing the certificate maintains a written record of the meaning of each symbol used in the
code, and
(ii) the record shall be made available to the distributor, retailer, consumer, and Commission upon request.
(2) A serial number may be used in place of a production lot identification on the helmet if it can serve as a
code to identify the production lot. If a bicycle helmet is manufactured for sale by a private labeler, and if the name
of the private labeler is on the certification label, the name of the manufacturer or importer issuing the certificate,
and the name and address of any foreign manufacturer, may also be in code.(ii) the record shall be made available to the distributor, retailer, consumer, and Commission upon request.
(e) Additional provisions for importers.
(1) General. The importer of any bicycle helmet subject to the standard in Subpart A of this Part 1203 must
issue the certificate of compliance required by § 14(a) of the CPSA and this section. If a reasonable testing
program meeting the requirements of this subpart has been performed by or for the foreign manufacturer of the product,
the importer may rely in good faith on such tests to support the certificate of compliance, provided:
(i) the importer is a resident of the United States or has a resident agent in the United States,
(ii) there are records of such tests required by § 1203.41 of Subpart C of this part, and
(iii) such records are available to the Commission within 48 hours of a request to the importer.
(2) Responsibility of importers. Importers that rely on tests by the foreign manufacturer to support the
certificate of compliance shall--in addition to complying with paragraph (e)(l)of this section--examine the records
supplied by the manufacturer to determine that they comply with § 1203.41 of Subpart C of this part.
(ii) there are records of such tests required by § 1203.41 of Subpart C of this part, and
(iii) such records are available to the Commission within 48 hours of a request to the importer.
Subpart C - - Recordkeeping
§ 1203.40 Effective date.
The recordkeeping requirements in this subpart are effective [insert date that is 1 year after publication] and apply
to bicycle helmets manufactured after that date.
§ 1203.41 Recordkeeping requirements.
(a) General. Every person issuing certificates of compliance for bicycle helmets subject to the standard in
Subpart A of this part shall maintain records which show that the certificates are based on a reasonable testing
program. The records shall be maintained for a period of at least 3 years from the date of certification of the last
bicycle helmet in each production lot. These records shall be available, upon request, to any designated officer or
employee of the Commission, in accordance with § 16(b) of the CPSA, 15 U.S.C. 2065(b). If the records are not
physically available during the inspection because they are maintained at another location, the firm must provide
them to the staff within 48 hours.
(b) Records of helmet tests. Complete test records shall be maintained. These records shall contain the following information.
(c) Format for records. The records required to be maintained by this section may be in any appropriate form or format that clearly provides the required information. Certification test results may be kept on paper, microfiche, computer disk, or other retrievable media. Where records are kept on computer disk or other retrievable media, the records shall be made available to the Commission on paper copies, or via electronic mail in the same format as paper copies, upon request.
(b) Records of helmet tests. Complete test records shall be maintained. These records shall contain the following information.
(1) an identification of the bicycle helmets tested;
(2) an identification of the production lot;
(3) the results of the tests, including the precise nature of any failures;
(4) a description of the specific actions taken to address any failures;
(5) a detailed description of the tests, including the helmet positioning index (HPI) used to define the proper position of the helmet on the headform;
(6) the manufacturer's name and address;
(7) the model and size of each helmet tested;
(8) identifying information for each helmet tested, including the production lot for each helmet;
(9) the environmental condition under which each helmet was tested, the duration of the helmet's conditioning, the temperatures in each conditioning environment, and the relative humidity and temperature of the laboratory;
(10) the peripheral vision clearance;
(11) a description of any failures to conform to any of the labeling and instruction requirements;
(12) performance impact results, stating the precise location of impact, type of anvil used, velocity prior to impact, and maximum acceleration measured in g's;
(13) the results of the positional stability test;
(14) the results of the dynamic strength of retention system test;
(15) the name and location of the test laboratory;
(16) the name of the person(s) who performed the test;
(17) the date of the test;
and
(18) the system check results.
(2) an identification of the production lot;
(3) the results of the tests, including the precise nature of any failures;
(4) a description of the specific actions taken to address any failures;
(5) a detailed description of the tests, including the helmet positioning index (HPI) used to define the proper position of the helmet on the headform;
(6) the manufacturer's name and address;
(7) the model and size of each helmet tested;
(8) identifying information for each helmet tested, including the production lot for each helmet;
(9) the environmental condition under which each helmet was tested, the duration of the helmet's conditioning, the temperatures in each conditioning environment, and the relative humidity and temperature of the laboratory;
(10) the peripheral vision clearance;
(11) a description of any failures to conform to any of the labeling and instruction requirements;
(12) performance impact results, stating the precise location of impact, type of anvil used, velocity prior to impact, and maximum acceleration measured in g's;
(13) the results of the positional stability test;
(14) the results of the dynamic strength of retention system test;
(15) the name and location of the test laboratory;
(16) the name of the person(s) who performed the test;
(17) the date of the test;
and
(18) the system check results.
(c) Format for records. The records required to be maintained by this section may be in any appropriate form or format that clearly provides the required information. Certification test results may be kept on paper, microfiche, computer disk, or other retrievable media. Where records are kept on computer disk or other retrievable media, the records shall be made available to the Commission on paper copies, or via electronic mail in the same format as paper copies, upon request.
Subpart D - - Requirements For Bicycle Helmets Manufactured
from March 17, 1995, Through __________________
[insert date that is 1 year after publication].
§ 1203.51 Purpose and basis.
The purpose and basis of this rule is to protect bicyclists from head injuries by ensuring that bicycle helmets
comply with the requirements of appropriate existing voluntary standards, as provided in 15 U.S.C. 6004(a).
1203.52 Scope and effective date.
(a) This Subpart D is effective March 16, 1995, except for §1203.53(a)(8), which is effective [insert date of
publication]. This Subpart D shall apply to bicycle helmets manufactured from March 17, 1995, through [insert date
that is 1 year after publication], inclusive. Such bicycle helmets shall comply with the requirements of one of the
standards specified in § 1203.53. This requirement shall be considered a consumer product safety standard
issued under the Consumer Product Safety Act.
(b) The term "bicycle helmet" is defined at § 1203.4(b).
(c) These interim mandatory safety standards will not apply to bicycle helmets manufactured after [insert date that is 1 year after publication]. Those helmets are subject to the requirements of Subparts A-C of this Part 1203.
(b) The term "bicycle helmet" is defined at § 1203.4(b).
(c) These interim mandatory safety standards will not apply to bicycle helmets manufactured after [insert date that is 1 year after publication]. Those helmets are subject to the requirements of Subparts A-C of this Part 1203.
§ 1203.53 Interim safety standards.
(a) Bicycle helmets must comply with one or more of the following standards, which are incorporated herein by
reference:
(b) This incorporation by reference was approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51. Copies of the standards may be obtained as follows. Copies of the ANSI Z90.4 standard are available from: American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd Street, 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036. Copies of the ASTM standards are available from: ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. Copies of the Canadian Standards Association CAN/CSA-D113.2-M89 standard are available from: CSA, 178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale (Toronto), Ontario, Canada, M9W 1R3. Copies of the Snell standards are available from: Snell Memorial Foundation, Inc., 6731-A 32nd Street, North Highlands, CA 95660. Copies may be inspected at the Office of the Secretary, Consumer Product Safety Commission, 4330 East-West Highway, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, or at the Office of the Federal Register, 800 N. Capitol Street NW, Room 700, Washington, DC.
(1) American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard Z90.4-1984, Protective Headgear for Bicyclists,
(2) ASTM standards F 1447-93 or F 1447-94, Standard Specification for Protective Headgear Used in Bicycling, incorporating the relevant provisions of ASTM F 1446-93 or ASTM F 1446-94, Standard Test Methods for Equipment and Procedures Used in Evaluating the Performance Characteristics of Protective Headgear, respectively,
(3) Canadian Standard Association standard, Cycling Helmets - CAN/CSA-D113.2-M89,
(4) Snell Memorial Foundation (Snell) 1990 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Bicycling (designation B-90),
(5) Snell 1990 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Bicycling, including March 9, 1994 Supplement (designation B-9OS),
(6) Snell 1994 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Non-Motorized Sports (designation N-94), or
(7) Snell 1995 standard for Protective Headgear for Use with Bicycles B-95.
(8) Subparts A-C of this Part 1203.
(2) ASTM standards F 1447-93 or F 1447-94, Standard Specification for Protective Headgear Used in Bicycling, incorporating the relevant provisions of ASTM F 1446-93 or ASTM F 1446-94, Standard Test Methods for Equipment and Procedures Used in Evaluating the Performance Characteristics of Protective Headgear, respectively,
(3) Canadian Standard Association standard, Cycling Helmets - CAN/CSA-D113.2-M89,
(4) Snell Memorial Foundation (Snell) 1990 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Bicycling (designation B-90),
(5) Snell 1990 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Bicycling, including March 9, 1994 Supplement (designation B-9OS),
(6) Snell 1994 Standard for Protective Headgear for Use in Non-Motorized Sports (designation N-94), or
(7) Snell 1995 standard for Protective Headgear for Use with Bicycles B-95.
(8) Subparts A-C of this Part 1203.
(b) This incorporation by reference was approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51. Copies of the standards may be obtained as follows. Copies of the ANSI Z90.4 standard are available from: American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd Street, 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036. Copies of the ASTM standards are available from: ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. Copies of the Canadian Standards Association CAN/CSA-D113.2-M89 standard are available from: CSA, 178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale (Toronto), Ontario, Canada, M9W 1R3. Copies of the Snell standards are available from: Snell Memorial Foundation, Inc., 6731-A 32nd Street, North Highlands, CA 95660. Copies may be inspected at the Office of the Secretary, Consumer Product Safety Commission, 4330 East-West Highway, Bethesda, Maryland 20814, or at the Office of the Federal Register, 800 N. Capitol Street NW, Room 700, Washington, DC.
Figures to Part 1203
Dated: ________________________, 1997.
Sadye E. Dunn,
Secretary, Consumer Product Safety Commission
End of CPSC DRAFT
Back to the top
Back to the Home Page